Mechanistically characterize novel ncRNA master regulators for cancer initiation, metastasis, immune response, and drug response. –Supported by NIH/NCI 1R01CA222274 (Yang, D) and ACS Research Scholar Grant 132632-RSG-18-179 (Yang, D).
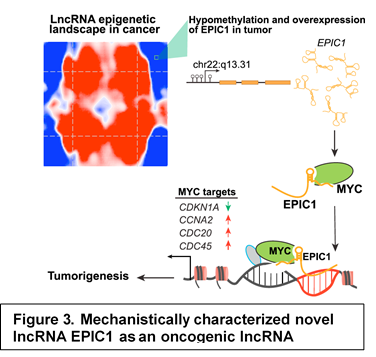
Identification of master regulating ncRNAs in cancer and the underlying mechanism is challenging. Our lab is capable of integrating the cancer genomics data and experimental validation to identify novel cancer-associated ncRNAs, modeling their down-stream regulatory network, and mechanistically validating their roles using cancer cell line and mouse models. We have functionally characterized seven master miRNAs for ovarian cancer EMT through regulating ZEB2 and SNAI2 (Cancer Cell, 2013). In gastric cancer, we successfully identified a key miRNA regulatory network for cancer metastasis and poor overall survival by targeting ZEB1 (Clinical Cancer Research, 2014 and PNAS, 2015). Our integrated strategy led to the discovery of miR-506 as a novel tumor suppressor in ovarian cancer by regulating cell senescence (J Pathol, 2014) and HR pathways (JNCI, 2015). Recently, through an integrated analysis of the lncRNA epigenetic landscape in 6475 tumor samples and 781 cancer cell lines, we have discovered a novel intergenic lncRNA gene, EPIC1, which is overexpressed and associated with poor survival in breast cancer. My group has cloned and functionally characterized this lncRNA. We have demonstrated that EPIC1 promotes breast cancer tumorigenesis (Cancer Cell, 2018, Fig. 3) and immune evasion (Science Advances, 2021; Science Signaling, under review) through directly interacting with MYC protein and enhancing its transcriptional activity.
- Yang D, Sun Y, Hu L, Zheng H, Ji P, Pecot CV, Zhao Y, Reynolds S, Cheng H, Rupaimoole R, Cogdell D, Nykter M, Broaddus R, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, Lopez-Berestein G, Liu J, Shmulevich I, Sood AK, Chen K, Zhang W. Integrated analyses identify a master microRNA regulatory network for the mesenchymal subtype in serous ovarian cancer. Cancer Cell. 2013 Feb 11;23(2):186-99. PubMed PMID: 23410973; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3603369.
- Song F*, Yang D*, Liu B*, Guo Y, Zheng H, Li L, Wang T, Yu J, Zhao Y, Niu R, Liang H, Winkler H, Zhang W, Hao X, Chen K. Integrated microRNA network analyses identify a poor-prognosis subtype of gastric cancer characterized by the miR-200 family. Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Feb 15;20(4):878-89. PubMed PMID: 24352645.
- Wang Z, Yang B, Zhang M, Guo W, Wu Z, Li S, Lee N, Xie W, Yang D#. LncRNA epigenetic landscape analysis identifies EPIC1 as an oncogenic lncRNA that interacts with MYC and promotes cell cycle progression in cancer, Cancer Cell. 2018 Apr 9;33(4):706-720.e9. PMID: 29622465.
- Wang Y, Fang Z, Hong M, Yang D#, Xie W#, Long-noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in drug metabolism and disposition, implications in cancer chemo-resistance, Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2020 January, Volume 10, Issue 1, Pages 105-112
- Pattarayan D, Wang Y, Wang Z, Li S, Wang X, Chen Y, Wang Y, Bhuniya A, Yadav G, Xie W, Kammula U, Li S, Zhang M#, Yang D#, LncRNA EPIC1 is a suppressor of cytoplasmic dsRNA type I interferon 1 signaling and a therapeutic target to enhance pembrolizumab response, Science Signaling, under review.